Introduction
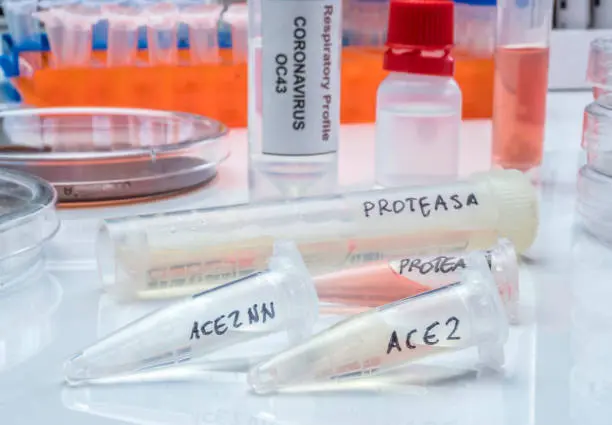
The global push for sustainability is no longer optional—it’s urgent. Industries from textiles to agriculture are under pressure to replace toxic chemicals and energy-intensive processes with planet-friendly alternatives. Enter enzymes: nature’s own catalysts, capable of accelerating reactions without harming ecosystems. At Genzyme Lifescience, we’re on a mission to unlock the full potential of enzymatic solutions, starting with our flagship innovation: alkaline protease.
While still in development, this enzyme promises to transform industries by offering a sustainable alternative to traditional, pollutant-heavy methods. But how exactly do enzymes like alkaline protease work, and why are they critical to a sustainable future? Let’s dive in
to stay informed!
Updates and Improvement
1. Enzymes: The Green Catalysts of Tomorrow
Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts, speeding up chemical reactions without being consumed. Unlike synthetic chemicals, they:
- Operate at mild conditions: Reducing energy demands (e.g., no high heat or pressure).
- Biodegrade safely: Leaving no toxic residues in soil or water.
- Target specificity: Minimizing waste by acting only on specific substrates.
Example: Proteases (like our alkaline protease) break down protein-based stains in detergents, replacing phosphate-laden chemicals that pollute waterways.
2. Genzyme’s Alkaline Protease: A Work in Progress
Our R&D team is engineering an alkaline protease that’s:
- Eco-optimized: Produced using renewable feedstocks and low-carbon fermentation.
- Industry-ready: Designed for scalability in sectors like detergents, leather processing, and waste management.
- Cost-effective: Balancing sustainability with affordability to drive mass adoption.
Behind the Scenes:
“We’re tweaking the enzyme’s stability and activity to outperform conventional options while ensuring zero ecological harm.”
– Mr. Saurabh Kalam, Lead Biotechnologist, Genzyme Lifescience
3. The Bigger Picture: Enzymes in Circular Bioeconomy
Enzymatic solutions are key to building a circular economy, where waste becomes a resource. For instance:
- Textile waste: Enzymes can break down polyester blends for recycling.
- Agriculture: Proteases convert organic waste into biofertilizers.
- Healthcare: Enzymes enable biodegradable drug delivery systems.
At Genzyme, we’re not just developing alkaline protease—we’re exploring microbial platforms to engineer enzymes for these frontier applications.
4. Challenges & Opportunities
While enzymes offer immense potential, barriers remain:
- Cost of production: Scaling sustainably requires innovative fermentation tech.
- Public awareness: Industries need education to transition from legacy systems.
Our Approach:
We’re partnering with academic labs and eco-conscious manufacturers to tackle these hurdles head-on.
5. What’s Next for Sustainable Enzymes?
The future is bright for green biotechnology. Trends to watch:
- AI-driven enzyme design: Accelerating discovery of novel catalysts.
- Policy shifts: Governments incentivizing enzyme-based solutions.
- Consumer demand: Brands adopting “enzyme-powered” as a sustainability badge.
At Genzyme, we’ll continue sharing updates on our alkaline protease journey and broader R&D efforts.
Join the Conversation
- What industries do YOU think need enzymatic solutions most?
- Have questions about alkaline protease or sustainable biotech?
Let’s connect: Drop a comment below or [reach out to our team]!
- Explore Our Mission: About us